I saw a news that about the Vuzix Smart Glasses M100 and it get a recipient of the CES (Consumer Electronics Show) Innovations 2013 Design and Engineering Award BEST OF INNOVATIONS, and selected as Best Technology in the Wireless Handset Accessory category. More information in following link.
http://www.vuzix.com/consumer/products_browse.html#video-eyewear
It's an interesting device but there are still challenges behind. Since Google launch their project glass, Vuzix is the 2nd company to make the similar product. So M100 get a lot of discussion even google guys go their booth to have it a look. According to the hardware specification from Vuzix web sites. It's totally an android based smart phone and the difference is the glasses appearance only. It's not special by just hardware specification only.
I think the story of this product is based on the intelligence functions like the video recognition, gesture recognition, voice recognition...etc. When these functions are introduced, this device become very interesting.
Vuzix also provide the SDK for developers and it may follow the smart phone pace to have variety of apps on the market.
So, let's look forward to it.
2013/02/20
2013/02/18
[工作點滴] AirVision 2.0 preview on Win7
Before the Chinese Lunar New Year, I got the latest alpha version of the AirVision2. It does not only inherit the pros from previous version but more quick and stable also. I just have some preview here about the installation and main pages showing.
After double clicking the windows installer, following the step of installation. When executing the airVision2, there is a windows security information pop up, please make sure the firewall does not block your application.
The airVision shows at the right bottom. Click the Launch a Browser to start a webpage for further.
First, we have to enter the name of the host PC name, language and position we are.
Second step, to create an account to accessing the airVision.
Third step, to add controller. If no, just go Next.
Finally, finish the first time configuration.
Login.
Clicking the unmanaged part of cameras and a list of unmanaged cameras show up.
Entering the information of the camera and clicking the Manage to make the connection.
Open the Map page.
Drag and drop the camera we want to the Map.
Same as the previous version, when detect motion, the color is change.
Add all the cameras on the Map we have.
We can see all the devices information in Devices page.
We can get the related statistics information in the Statistics page.
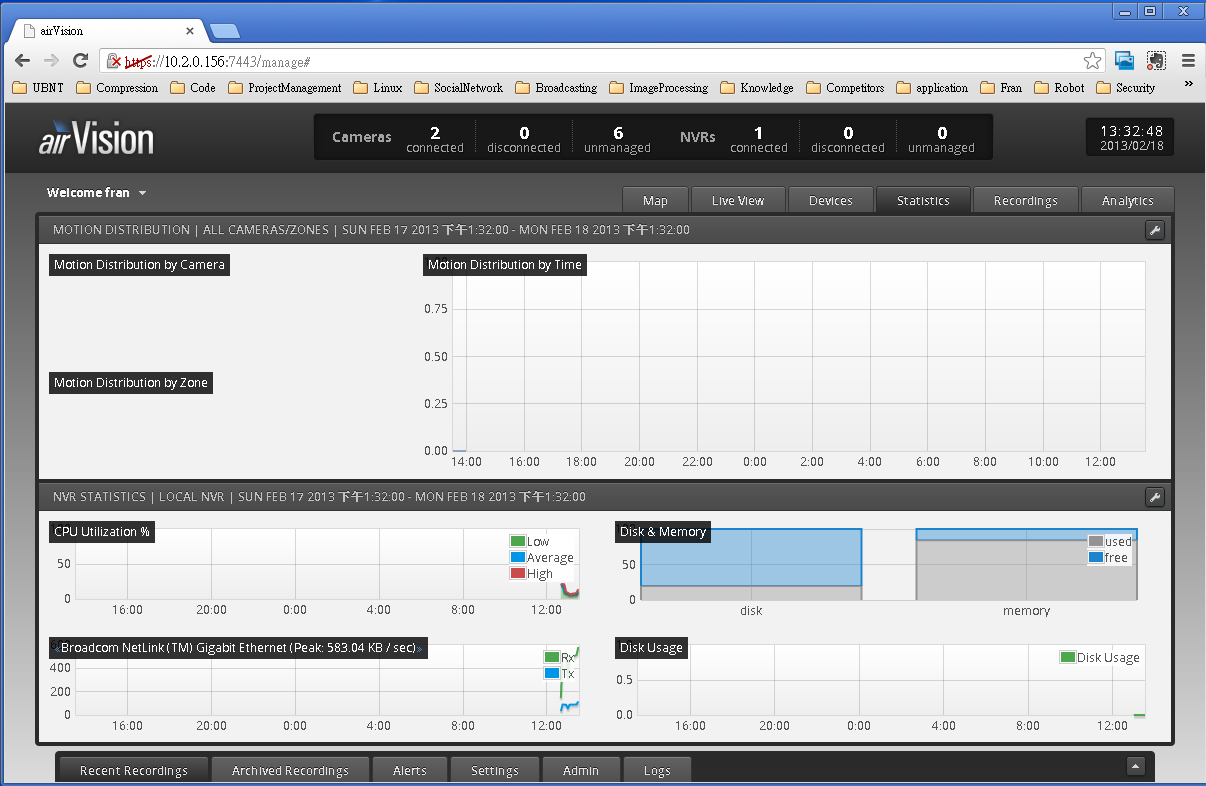
We can handle the recording in the Recordings page.
Analytics function as well.
The toggle bar at the bottom has lots of system information.
After quick playing, it's really over my expectation. Hope it can be launched soon.
There is a video demo on youtube for previous version. Maybe we can do comparisons in near future.
2013/02/17
[工作點滴] Miracast in surveillance system
Weeks ago, the supplier demo the Miracast function to us and my colleague told me maybe we can think if there are applications for surveillance system. At first I saw nothing special for surveillance application but I may find there is now.
Here is a capture picture from the whitepaper of WiFi alliance.
Basically, Miracast is a protocol and this means Miracast can be over any kind of infrastructure. However, Miracast connections are expected to be predominantly established between Wi-Fi devices connected with each other directly, without an AP acting as an intermediary. According to the topology, what we can see is a source to a sink and it is a peer-to-peer connection.
Go back to the topic we want to talk for surveillance. I plot a picture as follow, and this is just like a traditional surveillance system with cameras, recorder and monitor.
Now the connection part become the Miracast wifi direct to the adapter like NVR and play the video through HDMI to monitor finally. In future, the smart TV integrate the adapter and monitor part and link to cloud service as the picture.
If our target system is small with 4~8ch or under, this structure is quite simple and real for home, small store...etc. It's interesting and I'm looking forward to see it happen in near future.
Here is a capture picture from the whitepaper of WiFi alliance.
Basically, Miracast is a protocol and this means Miracast can be over any kind of infrastructure. However, Miracast connections are expected to be predominantly established between Wi-Fi devices connected with each other directly, without an AP acting as an intermediary. According to the topology, what we can see is a source to a sink and it is a peer-to-peer connection.
Go back to the topic we want to talk for surveillance. I plot a picture as follow, and this is just like a traditional surveillance system with cameras, recorder and monitor.
If our target system is small with 4~8ch or under, this structure is quite simple and real for home, small store...etc. It's interesting and I'm looking forward to see it happen in near future.
2013/02/16
[工作點滴] pure public or hybrid cloud for surveillance system?
The pure public cloud is no doubt that we build the web services on public and the hybrid combine the private part. According to the information on wiki, the public cloud aka external cloud is related to the service is provided by third party. There is a picture on wiki can describe exactly what we talk about.
Basically, there are four deployment models on wiki. The private cloud can't satisfy the requirements of the surveillance system. We do not talk about the community cloud also because it's not real on surveillance system.
There is a famous network camera company named Dropcam that deployment as pure public cloud system. When we install the the devices, we have to create an account and register them. As I know, Dropcam use the Amazon Web Service as the infrastructure. I just plot some simple block diagrams to describe it.
The way of Dropcam is the left bottom and all services are provided by Dropcam that host on AWS. The role of Dropcam become not only the device maker anymore but also service provider. The total system is the most easiest and simplest by this way.
The other three block diagrams are more and more complicated. Some surveillance company still want to expand their system base on the traditional type and the whole system may become the most complicated upper one. They will get into trouble soon.
There is still a question that not all people like to feed their private contents to service provider. That's why the original surveillance still there and get most market share but I think this situation will become different in recent years.
After studying, I'd like to shorten the deployment into two kinds. One is the Dropcam's way and the reason has already described above. Another one is because some weak points that the pure public can't overcome at this moment.
So which one is better, left or right? Let's wait and see what will happen next.
Basically, there are four deployment models on wiki. The private cloud can't satisfy the requirements of the surveillance system. We do not talk about the community cloud also because it's not real on surveillance system.
There is a famous network camera company named Dropcam that deployment as pure public cloud system. When we install the the devices, we have to create an account and register them. As I know, Dropcam use the Amazon Web Service as the infrastructure. I just plot some simple block diagrams to describe it.
The way of Dropcam is the left bottom and all services are provided by Dropcam that host on AWS. The role of Dropcam become not only the device maker anymore but also service provider. The total system is the most easiest and simplest by this way.
The other three block diagrams are more and more complicated. Some surveillance company still want to expand their system base on the traditional type and the whole system may become the most complicated upper one. They will get into trouble soon.
There is still a question that not all people like to feed their private contents to service provider. That's why the original surveillance still there and get most market share but I think this situation will become different in recent years.
After studying, I'd like to shorten the deployment into two kinds. One is the Dropcam's way and the reason has already described above. Another one is because some weak points that the pure public can't overcome at this moment.
So which one is better, left or right? Let's wait and see what will happen next.
2013/02/09
[心情隨筆] Happy lunar new year
Today is the end of the Dragon year and we use to have a good supper on this day. It's brand new lunar year tomorrow and we call it Snake year. Sometimes, we'd call it Small Dragon year rather than Snake year because because Dragon is much more significant in traditional.
Hope my family and friends have a brand new good Small Dragon Year.
Hope my family and friends have a brand new good Small Dragon Year.
2013/02/08
[工作點滴] I2S bus channels setting in gstreamer alsasrc plugin
My colleague did some experiments on gstreamer alsasrc and osssrc plugins and he found that alsasrc consume lots of cpu resource(around 16% on the chip we use). He asked me why the test tool that provided from chip vendor is quite efficient(around 1~2%). It was a big gap to me and I started to find why is that.
After hours checking, I found that the plugin may cause a busy wait in a while loop when the parameters set to non-blocking mode. I do a simple code modification and execute again but the cpu rate just lower to 12%. I'm a little frustrated about it but still had some enhancement.
So I started to try different parameters combination because he told that he found three differences from alsasrc plugin and the test code.
1. The setting of alsasrc is non-block mode but the test code is set to block mode.
2. The channels setting of alsasrc is 1 but the test code is set to 2.
3. The buffer size is limit in test code but alsasrc do not have that limit.
For 1: I thought the non-block mode should be much more efficient but the busy wait should change.
For 2: This is really weird because when I set the channels to be 2 in alsasrc plugin, the cpu rate become quite low. So I start to wondering if this is the characteristics of the I2S bus. I googled on the internet but did not find any information to describe that we have to set the channels parameter to be 2 in alsasrc plugin of gstreamer when the audio data bus is I2S. So I'll confirm it later.
For 3: I think it's reasonable to limit the buffer size.
After hours checking, I found that the plugin may cause a busy wait in a while loop when the parameters set to non-blocking mode. I do a simple code modification and execute again but the cpu rate just lower to 12%. I'm a little frustrated about it but still had some enhancement.
So I started to try different parameters combination because he told that he found three differences from alsasrc plugin and the test code.
1. The setting of alsasrc is non-block mode but the test code is set to block mode.
2. The channels setting of alsasrc is 1 but the test code is set to 2.
3. The buffer size is limit in test code but alsasrc do not have that limit.
For 1: I thought the non-block mode should be much more efficient but the busy wait should change.
For 2: This is really weird because when I set the channels to be 2 in alsasrc plugin, the cpu rate become quite low. So I start to wondering if this is the characteristics of the I2S bus. I googled on the internet but did not find any information to describe that we have to set the channels parameter to be 2 in alsasrc plugin of gstreamer when the audio data bus is I2S. So I'll confirm it later.
For 3: I think it's reasonable to limit the buffer size.
2013/02/07
[工作點滴] RabbitMQ setup and test
RabbitMQ setup and test
Server side:
My desktop PC is windows 7 and we download the rabbitmq server from http://www.rabbitmq.com/.
The installation guide is here http://www.rabbitmq.com/install-windows.html.
I use extra ethernet card and set the ip address to be 192.168.1.19 and make sure the firewall would not block the port 5672.
Client side: we put the send and listen on same device.
I use the package from https://github.com/alanxz/rabbitmq-c. We can follow the guide in the link to cross build and install on the embedded device we use.

 |
.png)
[工作點滴] The realtime of transport stream on Miracast
When I google the internet with realtime and transport stream, I could not find the information I want. The word 'realtime' must construct on the relative thinking. For example, there is camera and screen and the camera's video can be showed on the screen with quite small latency. We assume the latency is under 150ms or 300ms whatever and we can call this is realtime or not when we can have comparisons.
The structure of the transport stream or what we call MPEG-TS is not that simple. What I say is compare with raw encoded media direct push to intermedia. Maybe the transport stream is design for broadcasting usage, so the media stream can be selected and video can be smooth played are much more important than realtime. Because people would not feel any latency happened when they just watch TV.
If we want to convert raw encoded media to transport stream. First, we have to packetize the raw encoded media to packetized elementary stream(PES). Second, we handle the PES by the muxing, splitting to small slice AV data...etc to program stream or what we call transport stream. Finally, we send the transport stream to internet or satellite for people to receive and watch it on display. These steps create lots of latency and make us feel it's not realtime enough.
Let's go back to the definition of the Miracast. It is to convert the raw encoded media stream to transport stream and then encapsulate the stream to RTP. Finally go through the wifi directly to display. I'm not sure how many latency will be created? Maybe someone can tell me.
The structure of the transport stream or what we call MPEG-TS is not that simple. What I say is compare with raw encoded media direct push to intermedia. Maybe the transport stream is design for broadcasting usage, so the media stream can be selected and video can be smooth played are much more important than realtime. Because people would not feel any latency happened when they just watch TV.
If we want to convert raw encoded media to transport stream. First, we have to packetize the raw encoded media to packetized elementary stream(PES). Second, we handle the PES by the muxing, splitting to small slice AV data...etc to program stream or what we call transport stream. Finally, we send the transport stream to internet or satellite for people to receive and watch it on display. These steps create lots of latency and make us feel it's not realtime enough.
Let's go back to the definition of the Miracast. It is to convert the raw encoded media stream to transport stream and then encapsulate the stream to RTP. Finally go through the wifi directly to display. I'm not sure how many latency will be created? Maybe someone can tell me.
2013/02/05
[工作點滴] Airplay, DLNA and Miracast
Today, there is a supplier come to our company to introduce their solution with DLNA and Miracast support. I survey the internet and found three kinds of protocols are discussed on the market. The DLNA has been talked for a long time and Apple is DLNA member originally. But Apple left DLNA and create the proprietary Airplay protocol. The Miracast is created by Wifi Alliance. It seems that Android alliance choose the Miracast to fight with Apple?
且讓我們繼續看下去...
且讓我們繼續看下去...
[工作點滴] STL notes
國外工程師用boost c++ library來進行相關專案的開發, 進而看到一些相關的STL語法, 所以還是得抽空K一下相關資料, 至少要把code看懂.
The Standard Template Library (STL) is a C++ software library that influenced many parts of the C++ Standard Library. It provides four components called algorithms, containers, functional, and iterators.
The STL provides a ready-made set of common classes for C++, such as containers and associative arrays, that can be used with any built-in type and with any user-defined type that supports some elementary operations (such as copying and assignment). STL algorithms are independent of containers, which significantly reduces the complexity of the library.
The STL achieves its results through the use of templates. This approach provides compile-time polymorphism that is often more efficient than traditional run-time polymorphism. Modern C++ compilers are tuned to minimize any abstraction penalty arising from heavy use of the STL.
The STL was created as the first library of generic algorithms and data structures for C++, with four ideas in mind: generic programming, abstractness without loss of efficiency, the Von Neumann computation model, and value semantics.
Learning plot
訂閱:
文章 (Atom)

























